
- #WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD DRIVERS#
- #WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD VERIFICATION#
- #WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD PC#
- #WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD WINDOWS#
View objects in active directory – dsgetġ68.
#WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD DRIVERS#
Show the list of device drivers – driverqueryġ67. Import/Export data of an active directory – csvdeġ63. show the mapping inbetween logical and physical processor – coreinfoġ62. Copy one or more files to other location – copyġ61. Change the folder or go to a specific one – cdġ59. Manage the certification authority files and services – certutilġ58. Call another batch program using one – callġ57. Change the permissions of files – caclsġ56. Enable Or disable Break Capability in CMD – breakġ55. Manage the Background intelligent Transfer Service – bitsadminġ54.
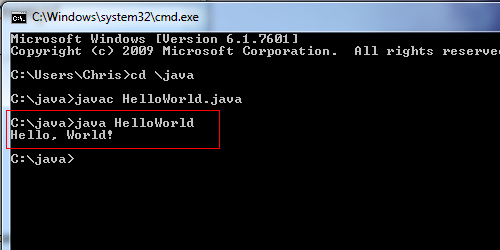
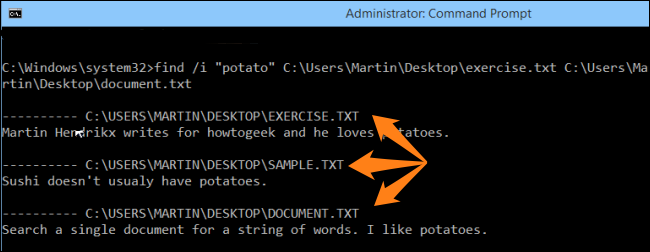
Finding for a strings in file – findstrġ53. Finding a text string in a file – findġ49. Replacing the files that are currently in use by the os – inuseġ48. Updating the Group policy settings – gpupdateġ46. Displaying the resultant set of Policy information – gpresultġ45. Importing or Exporting Active directory data – csvdeġ44. Deleting a folder and all subfolders – deltreeġ43. Showing the space used in folders – diskuseġ42. Know the file and volume utilities – fsutilġ41. Knowing the permissions for a user – permsġ39.
#WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD WINDOWS#
Opening the windows Explorer – explorerġ33. Displaying the list of files and folders – dirġ21. Converting FAT drives to NTFS – convertġ18. Compressing one or more files – compressġ15. Managing stored usernames/passwords – cmdkeyġ14. Encrypting or Decrypting Files/folders – cipherġ12.
Managing the Boot Configuration Data – bcdeditġ10. Windows Address Book Import Utility – wabmigġ08. User Account Management – nusrmgr.cplġ06. System Configuration Utility – msconfigġ03. Resultant Set of Policy (for xp professional) – rsop.mscĩ6. Removable Storage Operator Requests – ntmsoprq.mscĨ6. Phone and Modem Options – telephon.cplħ7. ODBC Data Source Administrator – odbccp32.cplħ3. Network Connections – control netconnectionsĦ6. Microsoft Syncronization Tool – mobsyncĦ1. Keyboard Properties – control keyboardĥ2.

Group Policy Editor (for xp professional) – gpedit.mscĤ5.
#WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD VERIFICATION#
File Signature Verification Tool – sigverifģ9. Files and Settings Transfer Tool – migwizģ1. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility – drwtsn32ģ0. Date and Time Properties – timedate.cplĢ7. Administrative Tools – control admintoolsġ7. However, if a malicious person gets a hold of the decryption keys and manages to decode your data, your data will be at risk.5. If your data is encrypted, it will remain secure even if it is openly available. Asymmetric encryption uses a public key and a private key to encrypt and decrypt data, whereas symmetric encryption uses just one key. There are two main types of encryption: symmetric encryption, and asymmetric encryption. Related: What Does Encrypted Mean and Is My Data Secure?
On the other, hand, decryption is the reverse process that converts obfuscated ciphertext into plain text that humans can read. Data is encrypted using specific algorithms which convert your data into ciphertext, safeguarding your data.Įncryption ensures that no unauthorized parties can access data that is not intended for them and is a fantastic option for protecting secure communications and preventing data breaches. Let's look at how you, too, can use command prompt to keep your files safe and secure.Įncryption, in short, keeps your data safe by obfuscating it, rendering it useless to unauthorized parties. Windows users can make use of the Command Prompt utility tool to secure their files from unauthorized access.
#WINDOWS SEARCH FOR TEXT IN FILES CMD PC#
If you are looking to secure your PC data, one method is to encrypt important files. In this digital age, it is crucial to keep your data safe from unauthorized misuse.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
